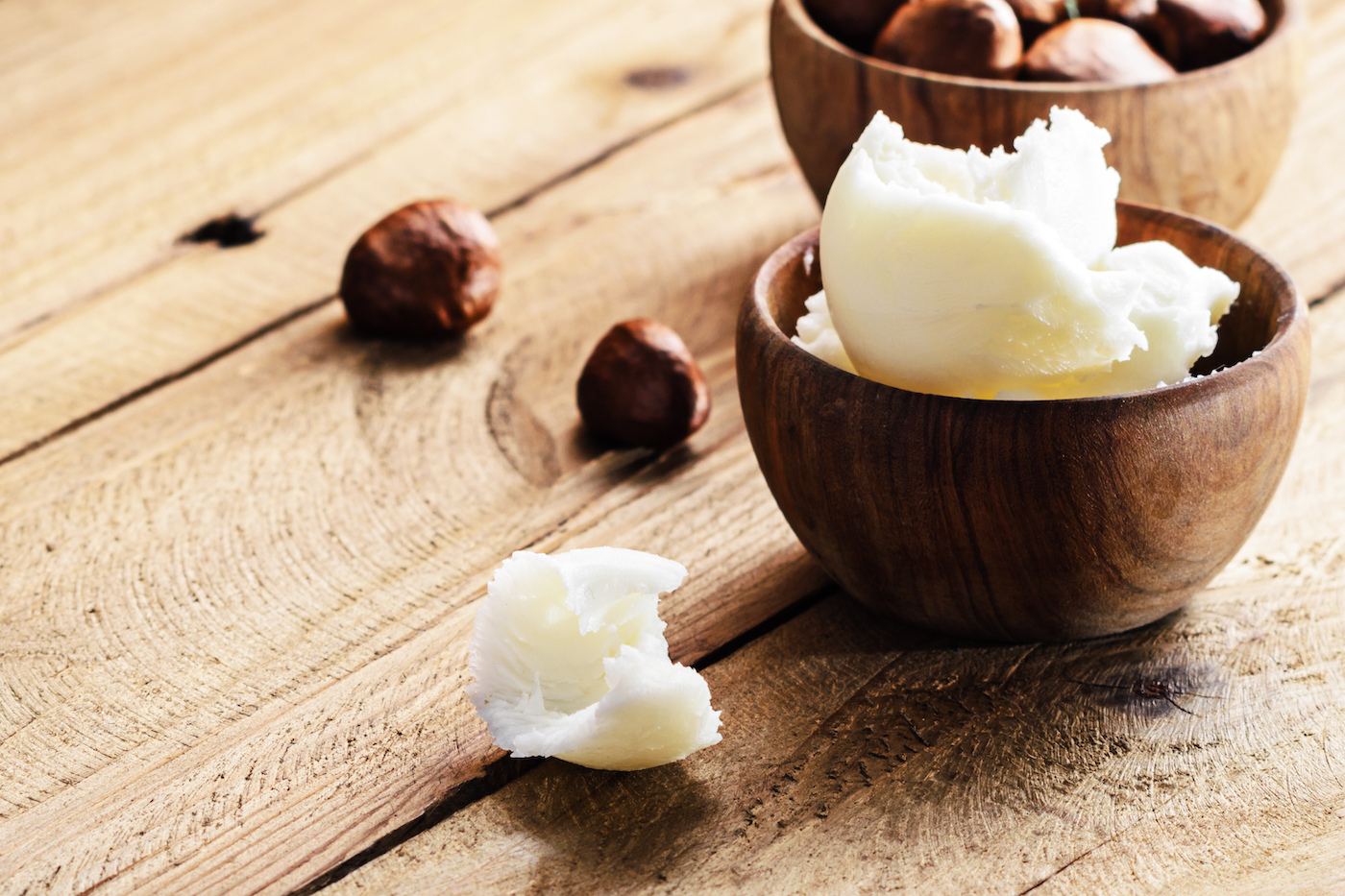
Natural cosmetic butters are derived from the extracts of numerous natural sources including seeds/kernels, beans, and nuts. They can be applied to the preferred area directly or after being incorporated into spa, cosmetic, or massage formulations, such as lotions, creams, soaps, lip balms, or salves, among other natural products to which they can be added. Butters melt on contact with body heat, adding additional softness and smoothness to skin and hair to relieve dryness, roughness, breakage, and irritation.
These ideal emollients are composed of varying amounts of active ingredients, fatty acids, solids, and semi-solid fat oils; thus, each butter exhibits distinct activities by virtue of its unique anti-inflammatory, soothing, moisturizing, and antioxidant properties. When added to natural product formulations and emulsions, they are known to contribute viscosity, stability, and sometimes hardness
COMPOSITION OF BUTTERS
Though not all the constituents listed below apply to all butter varieties, these are the main constituents in most varieties: Essential Fatty Acids, Vitamins, Proteins, Minerals, Antioxidants, Polyphenols, Phytosterols, and Tocopherol.
ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS are known to:
Produce and maintain the skin’s natural oil barrier
Hydrate skin to promote a supple, youthful appearance
Nourish cells and eliminate bodily toxins
Protect skin by creating an antimicrobial barrier against harsh environmental elements
Moisturize skin to prevent the premature signs of aging
Reduce water loss through the skin’s surface
Enhance the texture and softness of skin and hair
VITAMINS are known to:
Exhibit anti-aging properties
Enhance texture and tone
Fade and minimize the appearance of wrinkles and dark spots, such as under-eye circles
Smooth roughness
Strengthen and tighten skin’s protective outer layer to lock in moisture and protect against irritants
Protect against the harsh effects of UV radiation, such as redness, swelling, and dryness
Nourish and thicken hair
Reduce inflammation of the scalp, thereby preventing hair loss
PROTEINS are known to:
Repair and generate new tissues and cells
Slow the onset of the premature signs of aging, such as wrinkles and thinning hair
Contribute to the body’s immunity and to the strength and development of muscles
MINERALS are known to:
Protect against the stresses and harsh effects of environmental elements
Promote exfoliation
Balance and regulate oil production and moisture levels, especially for oily and sensitive skin and hair
Exhibit antioxidant properties
Tighten and smooth for a youthful appearance
Promote the growth of stronger hair that is thicker, hydrated, and lustrous
ANTIOXIDANTS are known to:
Boost circulation as well as cell metabolism, thereby calming inflammation
Tighten and tone the skin to prevent the appearance of wrinkles, blemishes, and scars
Plump out skin to smooth the look of fine lines and to blend in the newly developed skin
Improve the health of damaged skin by encouraging the growth of new cells for a rejuvenated look
Strengthen hair and maintain its health to prevent hair loss
POLYPHENOLS are known to:
Exhibit antioxidant activity
Increase hair growth
Show anti-aging properties, especially by reducing effects of UV-related damage
Exhibit photoprotective properties that help guard against UV radiation, harmful bacteria, oxidative stress, and harsh environmental conditions
Facilitate the renewal of skin cells
Prevent the breakdown of collagen, thereby restoring skin elasticity
Increase moisture levels for smoother skin and hair
PHYTOSTEROLS are known to:
Maintain cell structure, repair skin, and promote cell regeneration
Facilitate healing of dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, scars, sunburn, wind chapping, and wounds
Exhibit photoprotective properties / reduce photosensitivity
Facilitate skin cell metabolism and collagen production
Exhibit anti-inflammatory properties
Prevent itching and irritation
Boost immunity
Reduce hair loss and increase hair growth
TOCOPHEROL is known to:
Protect skin and hair against pollutants and harmful UV radiation
Tighten skin for a firmer look that diminishes signs of aging
Show natural preservative properties in skin care cosmetics and formulations
Moisturize and condition
Exhibit anti-inflammatory activity, which slows the look of aging
Facilitate the faster healing of wounds
EXTRACTING BUTTERS
Natural cosmetic body butters are blends of various oils that are made from beans, nuts, or seeds/kernels. The two main components of a butter are the minerals from their natural ingredients and the oils that carry the minerals to the areas of application. The combination of minerals and oils creates a barrier against harsh elemental factors that have drying effects. Butters typically do not contain water. If butters contained water, they would be emulsions, which are commonly known as “lotions.” A lack of water content also prevents the butters from needing synthetic chemicals to work as preservatives. The resultant texture of a butter can vary from soft and whipped, to semi-solid, to hard and solid.
CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR BUTTERS
Cosmetic butters should not be ingested and should not be stored within the reach of children, in case of accidental ingestion. Before the application of any butter, a patch test should be conducted on the inner arm or other generally insensitive area of skin, using a pea size amount of the butter to check for sensitivities. An absence of an allergic response within 48 hours indicates that the butter is safe to use.
Some butters may have adverse effects on skin that is prone to sensitivities, such as acne, as they tend to have a thicker, heavier, oilier, and longer-lasting finish on the skin compared to other emollients. Accordingly, body butters are best suited to skin that is dry, chapped, or broken. Individuals with allergies to the natural sources from which butters are derived are at a higher risk of developing an allergy to the butters themselves and should avoid their use. For example, individuals with nut allergies should avoid using butters sourced from nuts.
Potential side effects of cosmetic butters include skin irritation, hives, itching, rashes, swelling, and adult acne. In the event of an allergic reaction, discontinue use of the product and see a doctor, pharmacist, or allergist immediately for a health assessment and appropriate remedial action. To prevent these side effects, consult with a medical professional prior to use.
QUALITY OF BUTTERS
Organic butters are most commonly perceived to be of the highest quality, but even these will eventually go rancid over time. The quality of a butter can be determined by the following factors: Aroma, Method of Extraction, Consistency and Rate of Absorption, Natural Fatty Acids and Tocopherols, and Sun Protection Factor (SPF), among other characteristics.
AROMA Typically, butters are either odorless or they have mild, distinctive aromas that are faintly nutty, sweet, and/or characteristic of the plant material from which they are derived.
METHOD OF EXTRACTION The ideal butter for use in natural products is a Raw, Organic, Unrefined butter. Butters that are unrefined will have been filtered to eliminate dust or small particles (with few exceptions) without compromising the oil’s nutrients, vitamins, and fatty acids. Conversely, many cosmetic formulations require butters that are odorless so as not to interfere with the scents of the fragrance/essential oils that are added. For this purpose, Refined/Deodorized butters would be suitable.
CONSISTENCY AND ABSORPTION The consistency of various butters can be either thick or thin (hard or soft). The choice of either viscosity is a matter of personal preference. The intention behind using the butter will also be a determining factor in preference for consistency. For example, a light butter with fast absorption and an absence of a greasy residue would be a high-quality butter for oily skin or hair, as it would penetrate the skin and hair quickly without clogging pores. On the other hand, a rich, thick, deeply moisturizing butter is of better quality for treating severely dry and damaged skin or hair.
NATURAL FATTY ACIDS AND TOCOPHEROLS Butters contain beneficial and restorative fatty acids that lend the butters their nourishing and moisturizing properties. These are the constituents that offer regenerative and stimulating properties to promote the look and feel of younger, fresher, and healthier hair and skin. Tocopherols, such as natural Vitamin E, act as natural preservatives. Some butters have a high nutrient content but are too rich to use on their own or their scents are too overpowering. In these situations, they can be diluted in other emollients (e.g. Richer butters can be combined with lighter, odorless natural products). To customize and create the ideal butter, several butters can be blended to also change or combine their therapeutic properties before application.
SUN PROTECTION FACTOR (SPF) Some butters are naturally comprised of components, such as particular minerals, that offer protection against the sun’s UVB radiation. By reflecting or scattering UV rays, they prevent the rays from penetrating and burning the skin. When skin is damaged due to overexposure to the sun, this leads to premature signs of aging, such as wrinkles, fine lines, dark spots, and a leathery texture to the skin. Although it is not advisable to use cosmetic butters as replacements for other sun-protective agents, they can be used in combination with other products as part of a larger strategy to prevent photodamage.
STORING BUTTERS
Butters that are high in unsaturated fatty acid content will generally have a shorter shelf life and can last up to 6 months, whereas butters with a longer shelf life can last for at least 1-2 years. Natural cosmetic butters should be stored in the same manner as carrier oils; to maintain a butter’s quality and maximize its shelf life, it should be kept in an airtight container in a cool, dark place. Butters with natural antioxidant properties, such as those with high Vitamin E content, have longer shelf lives, as these constituents either prevent oxidation or slow down the process.
BUTTER PRICES
Butter prices depend on the types of plants from which they are derived, whether the plants are endemic or exotic, their botanical names, their therapeutic values, whether they undergo organic processing, the quantity being purchased, and the supplier it is purchased from.
USES & BENEFITS OF BUTTERS
Butters each have distinct combinations of properties that make them unique in form and function. The common factors shared by all butters includes their high emollience and their versatility, which allows them all to be used in a wide range of ways – massage, cleansing, softening, soothing, moisturizing, wound healing, protecting – on various parts of the body – hair, face, hands, and feet.
All butters can be applied to the skin directly or in blends to address issues of dryness, rashes, peeling, blemishes, wrinkles, itching, blistering, wound healing, cracking, roughness, stinging sensations, inflammation, aching, and fatigue, among other conditions. Butters are reputed to promote skin and hair health while contributing rejuvenating and regenerative properties.
For direct application to the skin, the ideal time to use butters for optimal absorption is when skin is damp after a shower. Additionally, butters can be applied to skin just before sleeping, as the length of the sleep cycle will allow the butter to penetrate into the skin more effectively for better hydration. Most natural butters melt on skin contact and will be absorbed quickly into the deep layers. Often concentrated, butters do not need to be applied in large amounts. Rather, it is best to begin by smoothing a pea-size amount of body butter across the preferred area of skin before gradually applying the same amount to other areas.
Natural butters can be added to cosmetic formulations as a base for moisturizers, or they can be added to other body butters to add more luxurious moisture. To ensure that they have been thoroughly incorporated, they should be vigorously stirred into formulations rather than simply shaking their containers, as butters have thicker consistencies than creams; thus, the additional essential oils and carrier oils should be folded into the butters just as cake batter is folded in on itself for optimal mixing. The recommended usage rate is 30 drops of essential oil and 5% carrier oils per 100 ml (3.40 oz.) of body butter base.
When the butters being used have strong scents, it is recommended that their Refined varieties be used to prevent the final product’s scent from being overpowered by their natural fragrances. Otherwise, Unrefined varieties are recommended for their beneficial constituents. Butters are already suitable for most, if not all, skin types; however, with the addition of a few drops of carrier oils and/or essential oils, they can be further customized to individual preference.